What is ECC RAM?
By Tan Lee Published on Apr 09, 2024 863
What is ECC RAM?
ECC RAM stands for Error-Correcting Code Random Access Memory. It's a type of computer memory that includes special circuitry to detect and correct errors that occur during data storage or retrieval. ECC RAM is commonly used in computer systems that require high stability, such as servers, workstations and other mission-critical systems where data integrity is extremely important.
The primary function of ECC RAM is to detect and correct single-bit errors that can occur due to various factors such as cosmic rays, electromagnetic interference, or manufacturing defects. Single-bit errors are the most common type of memory error, and ECC RAM can detect and correct them in real-time without disrupting the normal operation of the system.
ECC RAM achieves error correction by adding extra bits to each memory word (typically an extra parity bit or more sophisticated error correction codes). These extra bits are used to store redundant information that allows the memory controller to detect and correct errors when they occur.
What is ECC RAM commonly used for?
Under normal conditions without errors, ECC RAM will reload the entire previously transferred data stream. However, when an error occurs, RAM will request to resend the correct error packet. This mechanism of ECC RAM helps manage data and automatically correct errors, ensuring system stability as well as avoiding risks to the device.
ECC (Error-Correcting Code) RAM is commonly used in environments where data integrity and reliability are critical.
How ECC RAM works
ECC (Error-Correcting Code) RAM works by adding extra bits to memory words in order to detect and correct errors that may occur during data storage or retrieval. Here's how ECC RAM typically works:
Adding Redundant Bits: ECC RAM includes additional bits (parity bits or more sophisticated error correction codes) along with each memory word. These extra bits are used to store redundant information about the data being stored.
Error Detection: When data is written to ECC RAM, the memory controller calculates parity or checksum values based on the data being stored. These parity or checksum values are computed using various algorithms depending on the ECC scheme used.
Storing Redundant Information: The calculated parity or checksum values are stored alongside the actual data in memory. This redundant information enables the ECC RAM to detect errors when the data is read from memory.
Error Correction: When data is read from ECC RAM, the memory controller recalculates the parity or checksum values based on the data read from memory. If the recalculated values do not match the stored parity or checksum values, it indicates that an error has occurred.
Single-Bit Error Correction: ECC RAM can correct single-bit errors that occur during data retrieval. When a single-bit error is detected, the ECC RAM uses the redundant information stored alongside the data to correct the error automatically.
Multi-Bit Error Detection: In addition to single-bit error correction, ECC RAM can also detect multi-bit errors. While ECC RAM cannot correct multi-bit errors, it can detect them and alert the system to take appropriate action, such as resetting the affected component or initiating error recovery procedures.
Classification of ECC RAM
1. RAM Unbuffered ECC (RAM ECC UDIMM)
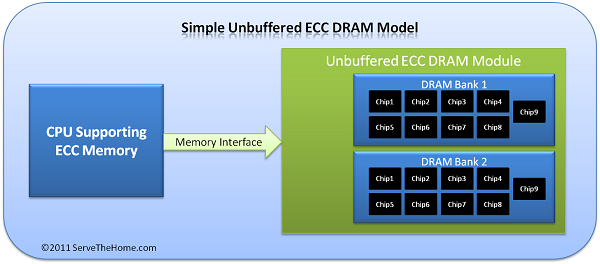
Unbuffered ECC RAM (ECC UDIMM RAM) belongs to the Unbuffered RAM type, does not use buffers or registers on the memory module. A special feature of this type of RAM is the integrated ECC (Error-Correcting Code) feature, allowing the ability to self-check and correct stored data errors. Compared to Registered ECC RAM, Unbuffered ECC RAM is highly appreciated for its memory access speed because there is no indirect transmission step via Registered chip.
2. RAM Registered ECC (RAM ECC RDIMM)
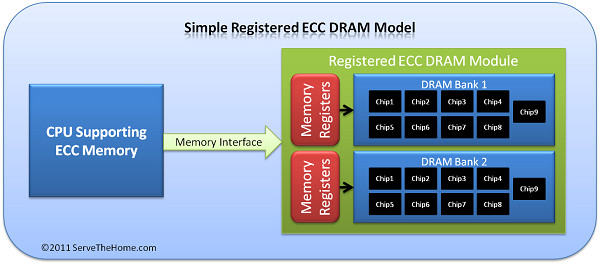
Registered ECC RAM (ECC RDIMM RAM) is a type of Registered RAM, expanded with the ECC (Error-Correcting Code) feature to self-check and correct errors during data storage. Registered RAM (RAM RDIMM) contains registers integrated directly on the memory module.
A special feature of Registered ECC RAM is the ability to re-direct (re-drive) signals through memory chips, allowing a module to contain more memory chips while still maintaining stability. Specifically, the access commands of Registered ECC RAM will be sent to the Registered chip before they are transmitted to the memory module.
Difference between regular RAM and ECC RAM
| Criteria | Regular RAM | RAM ECC UDIMM | RAM ECC RDIMM |
| Design | Has a beautiful design and can be equipped with additional heat sinks | Not beautiful, some types will have an aluminum heatsink cover and no LED lights | Not beautiful, some types will have an aluminum heatsink cover and no LED lights |
| Structure | There are no buffers or registers | There are memory access commands sent directly to the module | It contains registers mounted directly on the memory module |
| Number of memory chips | There are usually 8 memory chips and no chip in the middle | There are usually 9 chips per side and similar sizes | There are 10 front panel chips or 1 larger middle ECC chip |
| Code table | There is no letter E or R after the bandwidth specification | There is the letter E or ECC after the bandwidth parameter | There is usually the letter R after the bandwidth parameter |
Summary of advantages and disadvantages of ECC RAM
Here's a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of ECC (Error-Correcting Code) RAM:
Advantages:
Data Integrity: ECC RAM enhances data integrity by detecting and correcting errors that occur during data storage or retrieval. This feature is crucial in critical computing environments where data accuracy is paramount.
Reliability: ECC RAM improves system reliability by reducing the risk of data corruption, system crashes, and downtime caused by memory errors. It helps ensure uninterrupted operation, particularly in servers, workstations, and mission-critical systems.
Error Detection and Correction: ECC RAM can detect and correct single-bit errors in real-time, preventing these errors from propagating and causing system instability or data loss. It provides an additional layer of protection against transient memory errors.
Enhanced Performance in Error-Prone Environments: In environments where memory errors are more likely to occur due to factors like cosmic radiation or high operating temperatures, ECC RAM can maintain system stability and performance by effectively handling errors.
Disadvantages:
Cost: ECC RAM is generally more expensive than non-ECC RAM due to the additional hardware and complexity required for error detection and correction. The higher cost of ECC RAM may be a barrier for budget-constrained consumers or organizations.
Slight Performance Overhead: ECC RAM may introduce a slight performance overhead compared to non-ECC RAM due to the additional processing required for error correction. While the impact on overall system performance is often minimal, it can be a consideration for applications where every bit of performance matters.
Limited Availability: ECC RAM may not be as widely available as non-ECC RAM, especially in consumer-grade desktops, laptops, and gaming systems.
Compatibility Issues: Some systems may not support ECC RAM or may require specific motherboard chipsets to enable ECC functionality.
- How to Create a Metro GridView in C#
- How to Get the amount of RAM available on the System in C#
- How to Download and Install Metro Framework
- How to undo the changes in Entity Framework
- How to create a Metro Message Box in C#
- How to use Modern UI Metro Framework in C#
- Object Services Layer in Entity Framework
- Improving Entity Framework performance