How to secure ASP.NET Core with NWebSec
By Tan Lee Published on Nov 07, 2024 787
First, you need to install the NWebSec.AspNetCore.Middleware NuGet package. This package provides middleware to add security headers to your application.
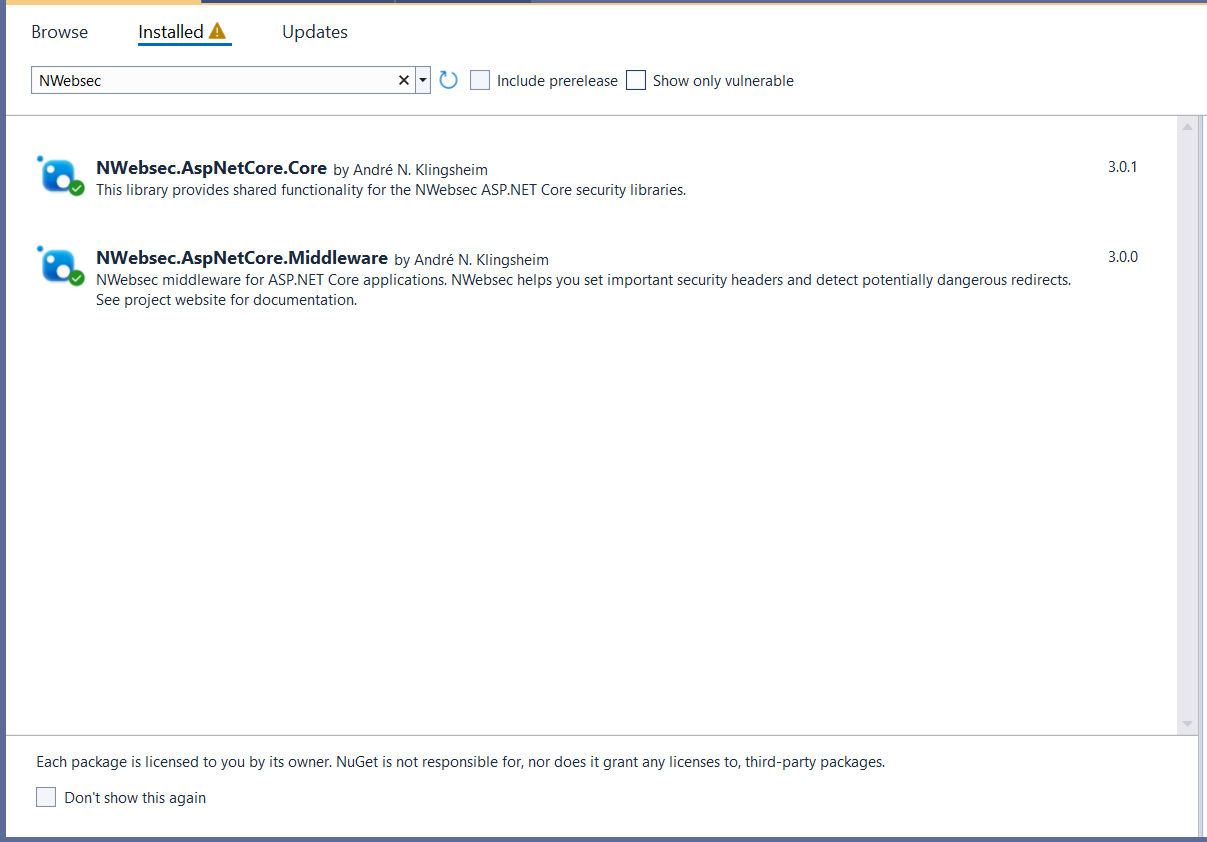
You can run the following command in your terminal or package manager console:
Install-Package NWebSec.AspNetCore.Middleware
What secure HTTP response headers can do?
- Protect web resources by ensuring that only authorized users can access them.
- Make it as difficult as possible for potential attackers to extract sensitive information from your website.
Let's explore the security headers supported by major browsers to enhance the protection of your web application.
- [HSTS] HTTP Strict Transport Security Header
- X-XSS-Protection Header
- X-Frame-Options Header
- [CSP] Content-Security-Policy Header
- X-Content-Type-Options Header
- Referrer-Policy HTTP Header
- Remove the X-Powered-By Header
To configure NWebSec, you will need to modify the Program.cs file as follows:
[HSTS] HTTP Strict Transport Security Header
builder.Services.AddHsts(options =>
{
options.Preload = true;
options.IncludeSubDomains = true;
options.MaxAge = TimeSpan.FromDays(365);
});
if (app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.ConfigureExceptionHandler(logger);
app.UseMigrationsEndPoint();
}
else
{
app.ConfigureExceptionHandler(logger);
//The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseForwardedHeaders();
//HTTP Strict Transport Security Header
app.UseHsts();
//...
}X-XSS-Protection Header
This prevents pages from loading in modern browsers if reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) is detected. However, it is often unnecessary if the site already implements a strong Content-Security-Policy (CSP).
//X-XSS-Protection Header app.UseXXssProtection(options => options.EnabledWithBlockMode());
X-Frame-Options Header
This header ensures that site content cannot be embedded in an iframe on other websites, helping to prevent clickjacking attacks.
//X-Frame-Options Header app.UseXfo(options => options.SameOrigin());
[CSP] Content-Security-Policy Header
Just like locking all the doors to protect your home and sharing the key only with your family, the Content-Security-Policy (CSP) header allows you to whitelist trusted resource origins when your site is loaded. The configuration of this policy can vary greatly depending on your specific security requirements.
app.UseCsp(opts => opts
.BlockAllMixedContent()
.StyleSources(s => s.Self())
.StyleSources(s => s.UnsafeInline())
.FontSources(s => s.Self())
.FormActions(s => s.Self())
.FrameAncestors(s => s.Self())
.ImageSources(s => s.Self())
.ScriptSources(s => s.Self())
);or
app.UseCsp(options => options.DefaultSources(s => s.Self()
.CustomSources("data:")
.CustomSources("https:"))
.StyleSources(s => s.Self()
.CustomSources("apis.google.com", "cdn.datatables.net", "cdnjs.cloudflare.com", "cdn.jsdelivr.net", "fonts.googleapis.com", "cdn.plyr.io")
.UnsafeInline()
)
.ScriptSources(s => s.Self()
.CustomSources("cdn.plyr.io", "cdn.jsdelivr.net", "www.paypal.com", "www.paypalobjects.com", "www.googletagmanager.com", "cdnjs.cloudflare.com", "cdn.datatables.net")
.UnsafeInline()
.UnsafeEval()
));X-Content-Type-Options Header
Attackers can manipulate innocent MIME types (e.g., text/css) and change them into executable types, potentially causing serious damage to your site or users.
//X-Content-Type-Options Header app.UseXContentTypeOptions();
Referrer-Policy Http Reader
This header controls how much information is sent in the Referer (misspelled as "Referer") header field. The default value is `no-referrer-when-downgrade`, meaning no referrer data is sent if the security protocol is downgraded, such as when navigating from an HTTPS to an HTTP site.
//Referrer-Policy Http Reader app.UseReferrerPolicy(options => options.NoReferrerWhenDowngrade());
Remove X-Powered-By Header
To prevent disclosing information about the web server or technology in use (e.g., ASP.NET, Kestrel), we should remove the X-Powered-By header. This can be done by modifying the `web.config` file.
<system.web>
<httpRuntime enableVersionHeader="false"/>
</system.web>
<system.webServer>
...
<httpProtocol>
<customHeaders>
<remove name="X-Powered-By" />
</customHeaders>
</httpProtocol>
</system.webServer>In ASP.NET Core, you can disable the X-Powered-By header by setting the `AddServerHeader` option of `.UseKestrel()` to `false` (the default is `true`).
builder.WebHost.ConfigureKestrel(serverOptions =>
{
serverOptions.AddServerHeader = false;
});- Implement security headers for an ASP.NET Core
- How to add security headers to an ASP.NET Core Application
- How to Initialize TagHelpers in ASP.NET Core with Shared Data
- Boost Your ASP.NET Core Website Performance with .NET Profiler
- The name 'Session' does not exist in the current context
- Implementing Two-Factor Authentication with Google Authenticator in ASP.NET Core
- How to securely reverse-proxy ASP.NET Core
- How to Retrieve Client IP in ASP.NET Core Behind a Reverse Proxy