Implement security headers for an ASP.NET Core
By Tan Lee Published on Jun 24, 2025 49
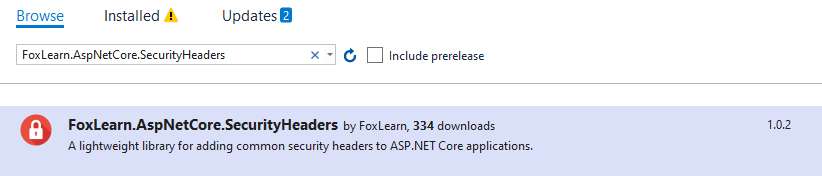
FoxLearn.AspNetCore.SecurityHeaders is a lightweight library for adding common security headers to ASP.NET Core applications.

After publishing your website, you can use https://securityheaders.com to test your security headers.
This package simplifies the process of applying essential HTTP security headers such as Content-Security-Policy, Strict-Transport-Security, X-Content-Type-Options, and more to your ASP.NET Core middleware pipeline, helping protect your web applications from common vulnerabilities.
You can install the package via the .NET CLI:
dotnet add package FoxLearn.SecurityHeaders.AspNetCore
Or via the NuGet UI in Visual Studio by searching for FoxLearn.AspNetCore.SecurityHeaders
To enable and customize security headers in your ASP.NET Core application, configure the services and middleware using the provided extension methods. Add the service registration in your Startup.cs or Program.cs file:
builder.Services.AddSecurityHeaderPolicies(options =>
{
options.AddCrossOriginResourcePolicy(x => x.SameOrigin())
.AddFrameOptionsDeny()
.AddContentTypeOptionsNoSniff()
.AddReferrerPolicy(ReferrerPolicy.StrictOrigin)
.AddStrictTransportSecurity()
.AddPermissionsPolicy(policy =>
{
policy.AddAccelerometer().Self().For("https://foxlearn.com");
policy.AddMicrophone();
});
});
var app = builder.Build();
...
app.UseSecurityHeaders(); // RequiredTo fully control the headers returned, create a HeaderPolicyCollection and define your own set of headers including any custom headers you may need:
// Define a custom header policy
var policy = new HeaderPolicyCollection()
.AddFrameOptionsDeny()
.AddReferrerPolicyStrictOriginWhenCrossOrigin();
builder.Services.AddSecurityHeaderPolicies(options =>
{
options.AddPolicy("CustomPolicy", policy => policy.AddCustomHeader("X-Custom", "SomeValue"));
});
// Apply your custom policy globally or on a per-endpoint basis:
app.UseSecurityHeaders(policy); // Apply custom global policy
app.UseEndpointSecurityHeaders(); // Enable attribute-based usageNext, Apply a Policy to a Controller Action
public class HomeController : Controller
{
private readonly ILogger<HomeController> _logger;
public HomeController(ILogger<HomeController> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
[SecurityHeadersPolicy("CustomPolicy")]
public IActionResult Index()
{
return View();
}
}Apply custom policies to endpoints
If you need to apply a custom (non-default) security header policy to a specific endpoint, use the .WithSecurityHeadersPolicy("PolicyName") extension method during endpoint mapping:
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello world")
.WithSecurityHeadersPolicy("CustomPolicy"); // Apply a named policy to this endpointIf you're using Kestrel, the Server header can be removed in the Program class. For IIS, you’ll likely need to remove it via the web.config file.
builder.WebHost.ConfigureKestrel(serverOptions =>
{
serverOptions.AddServerHeader = false;
});
- How to Initialize TagHelpers in ASP.NET Core with Shared Data
- Boost Your ASP.NET Core Website Performance with .NET Profiler
- The name 'Session' does not exist in the current context
- Implementing Two-Factor Authentication with Google Authenticator in ASP.NET Core
- How to securely reverse-proxy ASP.NET Core
- How to Retrieve Client IP in ASP.NET Core Behind a Reverse Proxy
- Only one parameter per action may be bound from body in ASP.NET Core
- The request matched multiple endpoints in ASP.NET Core