How to Create Word Document in C#
By Tan Lee Published on Jan 17, 2025 581
Creating a Word document programmatically in C# can be achieved using the Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word library.
This library allows you to interact with Microsoft Word, enabling you to create, modify, and save Word documents directly from your C# application.
Prerequisites
Before diving into the code, ensure the following prerequisites are met:
- Microsoft Office Installation: MS Office must be installed on your machine.
- Project Setup: Create a Console or Windows application in Visual Studio.
- Add Reference: Add a reference to the
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Wordlibrary.
You can find this DLL at:
C:\Windows\assembly\GAC_MSIL\Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word\15.0.0.0__71e9bce111e9429c\Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.dll.
Below is a sample implementation of creating a Word document with a header, content, and a table.
For example, word c# document create
private void CreateWordDocument(string header, string wholeData)
{
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application winword = null;
Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document = null;
try
{
// Initialize Word application
winword = new Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Application
{
ShowAnimation = false,
Visible = false
};
// Create a new document
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
document = winword.Documents.Add(ref missing, ref missing, ref missing, ref missing);
// Add Header
AddParagraph(document, header, "Heading 1");
// Add Content
AddParagraph(document, wholeData, fontSize: 14);
// Add Table
AddSampleTable(document);
// Save Document
string sanitizedHeader = ReplaceInvalidFileNameChars(header);
string filePath = $@"C:\YourOutputPath\{sanitizedHeader}.docx";
document.SaveAs2(filePath);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {ex.Message}");
}
finally
{
// Cleanup
document?.Close(false);
winword?.Quit(false);
}
}
private void AddParagraph(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document, string text, string style = null, int? fontSize = null)
{
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
var paragraph = document.Content.Paragraphs.Add(ref missing);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(style))
{
paragraph.Range.set_Style(style);
}
if (fontSize.HasValue)
{
paragraph.Range.Font.Size = fontSize.Value;
}
paragraph.Range.Text = text;
paragraph.Range.InsertParagraphAfter();
}
private void AddSampleTable(Microsoft.Office.Interop.Word.Document document)
{
object missing = System.Reflection.Missing.Value;
var range = document.Content.Paragraphs[1].Range; // Use the first paragraph's range
var table = document.Tables.Add(range, 2, 1, ref missing, ref missing);
table.Borders.Enable = 1;
foreach (Row row in table.Rows)
{
foreach (Cell cell in row.Cells)
{
if (cell.RowIndex == 1)
{
cell.Range.Text = $"Sample Code {cell.ColumnIndex}";
cell.Range.Font.Bold = 1;
cell.Range.Font.Name = "Verdana";
cell.Shading.BackgroundPatternColor = WdColor.wdColorGray25;
cell.VerticalAlignment = WdCellVerticalAlignment.wdCellAlignVerticalCenter;
cell.Range.ParagraphFormat.Alignment = WdParagraphAlignment.wdAlignParagraphCenter;
}
else
{
cell.Range.Text = "SQL or C# code sample will appear here";
}
}
}
}
private string ReplaceInvalidFileNameChars(string input)
{
return string.Concat(input.Select(c => Path.GetInvalidFileNameChars().Contains(c) ? ' ' : c));
}Usage
CreateWordDocument("MyHeader", "This is the content of the document.");In this example:
- Header and Content: The
Paragraphobjects are used to add headers and content with specific styles and formatting. - Table Creation: A 1x2 table is created using the
Tables.Addmethod, where each cell can contain custom text and formatting. - File Saving: The file is saved with a name derived from the
headerparameter. Special characters are removed to avoid errors.
Categories
Popular Posts
HTML Bootstrap 4 Login, Register & Reset Template
Nov 11, 2024
Material Lite Admin Template
Nov 14, 2024
Horizon MUI Admin Dashboard Template
Nov 18, 2024
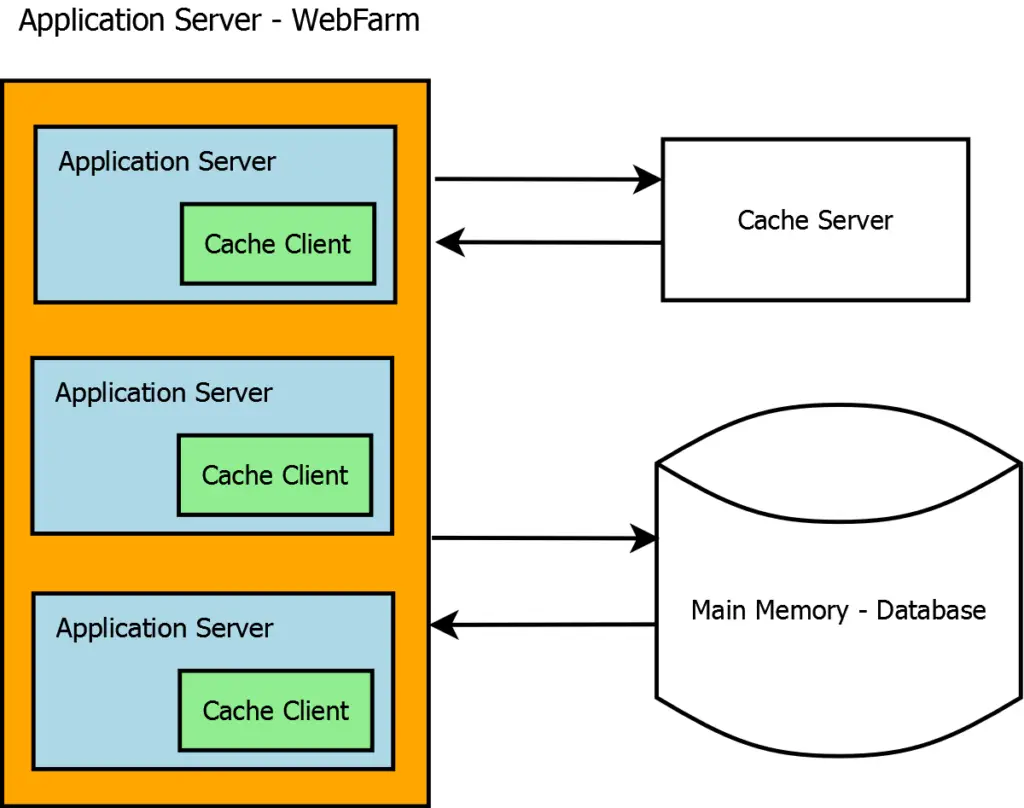
Implementing Caching in ASP.NET Core
Dec 14, 2024