How to Create a Metro Login form with SQL Server in C#
By Tan Lee Published on Jun 19, 2017 7.44K
This article provides a step-by-step guide to creating a Metro-style login form in C# using SQL Server as the database backend. We'll implement user authentication and show how to transition between a login form and the main application interface.
How to Create a Metro Login form with SQL Server in C#?
Open Visual Studio, then click New Project, then select Visual C# on the left, then Windows and then select Windows Forms Application. Name your project "MetroLoginForm" and then click OK
Right click on your project select Manage NuGet Packages -> Search metro framework -> Install

If you don't see the metro framework in your toolbox, you can view How to download and install metro framework
Design metro form as shown below.
Your login form name: frmLogin
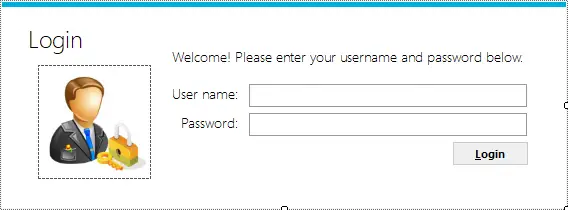
Your main form name: frmMain
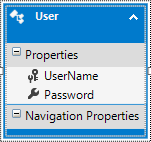
Add an EF model to your project as below
Run the following script in SQL Server to create a Users table:
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[Users]( [UserName] [varchar](25) NOT NULL, [Password] [varchar](50) NULL, CONSTRAINT [PK_Users] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED ( [UserName] ASC )WITH (PAD_INDEX = OFF, STATISTICS_NORECOMPUTE = OFF, IGNORE_DUP_KEY = OFF, ALLOW_ROW_LOCKS = ON, ALLOW_PAGE_LOCKS = ON) ON [PRIMARY] ) ON [PRIMARY]
Add code to handle your form
The frmMain class represents the main application interface displayed after a successful login.
using System;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MetroLoginForm
{
public partial class frmMain : MetroFramework.Forms.MetroForm
{
bool _logOut;
public frmMain(string userInfo)
{
InitializeComponent();
// Display logged-in user information
lblUserInfo.Text = userInfo;
}
private void lnkLogOut_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
_logOut = true; // Set logout flag
this.Close(); // Close the main form
frmLogin.Instance.Show(); // Show login form
}
private void frmMain_FormClosed(object sender, FormClosedEventArgs e)
{
// If not logging out, exit application
if (!_logOut)
Application.Exit();
}
}
}The frmLogin class handles user authentication and transitions to the main form on successful login.
using System;
using System.Data;
using System.Linq;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace MetroLoginForm
{
public partial class frmLogin : MetroFramework.Forms.MetroForm
{
static frmLogin _instance;
// Singleton pattern to ensure only one instance of frmLogin exists
public static frmLogin Instance
{
get
{
if (_instance == null)
_instance = new frmLogin();
return _instance;
}
}
public frmLogin()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void frmLogin_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
_instance = this; // Assign the current instance
txtUsername.Focus(); // Set focus to the username textbox
}
private void btnLogin_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Validate input
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(txtUsername.Text))
{
MetroFramework.MetroMessageBox.Show(this, "Please enter your username.", "Message", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
txtUsername.Focus();
return;
}
try
{
using(DbUserEntities db = new DbUserEntities())
{
// LINQ query to check if the user exists
var query = from u in db.Users
where u.UserName == txtUsername.Text && u.Password == txtPassword.Text
select u;
if (query.SingleOrDefault() != null)
{
// Hide login form and show main form
this.Hide();
frmMain frm = new frmMain(string.Format("Login with: {0}", txtUsername.Text));
frm.ShowDialog();
}
else
MetroFramework.MetroMessageBox.Show(this, "Your username or password is incorrect.", "Message", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{
MetroFramework.MetroMessageBox.Show(this, ex.Message, "Message", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
}
}The DbUserEntities class represents the Entity Framework (EF) context for database access. Configure it with your database connection string and the Users table mapping.
VIDEO TUTORIAL





