How to Multithreading in C#
By Tan Lee Published on May 14, 2024 11.14K
The advantage of threading is the ability to create applications that use more than one thread of execution. For example, a process can have a user interface thread that manages interactions with the user and worker threads that perform other tasks while the user interface thread waits for user input.
How to use MultiThreading in C#
Using multithreading in C# Windows Forms applications can improve responsiveness and performance, especially for long-running tasks that might otherwise freeze the user interface.
Here's a basic guide on how to use multithreading in C# Windows Forms.
Open your Visual Studio, then click New Project, then select Visual C# on the left, then Windows and then select Windows Forms Application. Name your project "MultiThread" and then click OK button.
Drag and drop Button controls from the Visual Studio toolbox onto your form designer, then design your form as shown below.
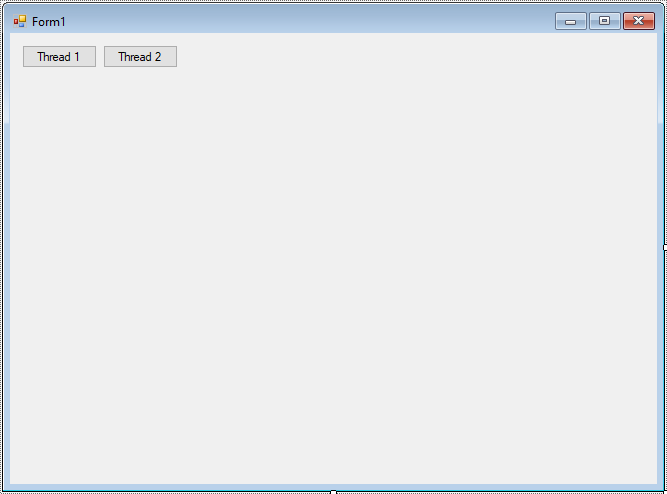
Adding a Form_Load event handler that allows you to initiate random drawing circles.
Random rd;
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
rd = new Random();
}How you can create and start a thread in C#
Add code to handle button clicks allows creating 2 threads to draw circles as shown below.
private void btnThread1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Create a new thread and pass a method to be executed by the thread
Thread thread = new Thread(t =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
int width = rd.Next(0, this.Width);
int height = rd.Next(50, this.Height);
this.CreateGraphics().DrawEllipse(new Pen(Brushes.Red, 1), new Rectangle(width, height, 10, 10));
//Delay
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
})
{ IsBackground = true };
// Start the thread
thread.Start();
}
private void btnThread2_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//Start new thread
Thread thread = new Thread(t =>
{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
int width = rd.Next(0, this.Width);
int height = rd.Next(50, this.Height);
this.CreateGraphics().DrawEllipse(new Pen(Brushes.Blue, 1), new Rectangle(width, height, 10, 10));
//Delay
Thread.Sleep(100);
}
})
{ IsBackground = true };
thread.Start();
}In C#, a thread is the smallest unit of execution that can be scheduled by the operating system. Threads allow a program to perform multiple tasks concurrently, enabling tasks to run in parallel.
VIDEO TUTORIAL