How to record audio from microphone in C#
By Tan Lee Published on Jul 13, 2024 3.37K
NAudio is an open source .NET audio library written by Mark Heath. Here's a basic example of how you can record audio from a microphone using NAudio:
How to record audio from microphone in C#?
NAudio support multiple features:
- Play back audio using a variety of APIs (WaveOut, DirectSound, ASIO, WASAPI)
- Read audio from many standard file formats (WAV, AIFF, MP3, G.711 mu-law and a-law, ADPCM, G.722, Speex (using NSpeex),WMA, AAC, MP4 and more)
- Convert between various forms of uncompressed audio (Change the number of channels - Mono to stereo, stereo to mono, Modify bit depth (8, 16, 24, 32 integer or 32 bit IEEE float), Resample audio using a choice of resampling algorithms)
- Encode audio using any ACM or Media Foundation codec installed on your computer (Create MP3s (Windows 8 and above), AAC/MP4 audio (Windows 7 and above), WMA WAV files containing G.711, ADPCM, G.722, etc.)
- Mix and manipulate audio streams using a 32-bit floating mixing engine
- Record audio using a variety of capture APIs (WaveIn, WASAPI, ASIO)
- Record system audio with WASAPI Capture
- Work with soundcards (Enumerate devices, Access soundcard controls and metering information)
- Full MIDI event model (Read and write MIDI files, Respond to received MIDI events, Send MIDI events)
- An extensible programming model (All base classes easily inherited from for you to add your custom components)
- Support for UWP (Create Windows 8 Store apps and Windows Universal apps)
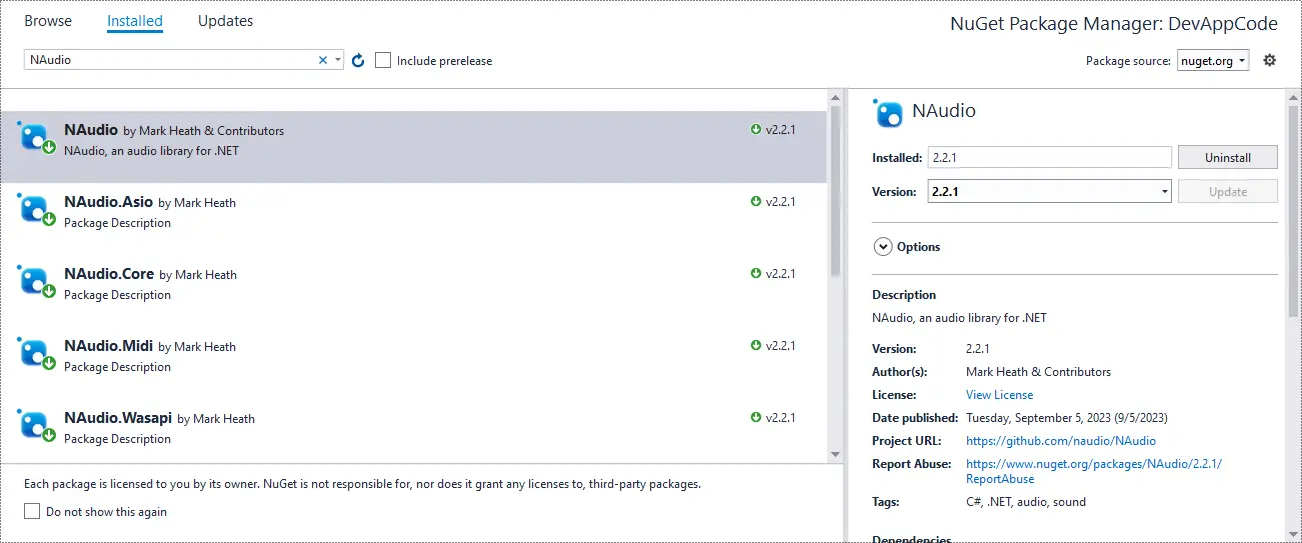
First, You can design a simple UI as shown below, then you need to install the NAudio package from NuGet if you haven't already.
If you install it via NuGet Package Manager Console
Install-Package NAudio
You can also install NAudio via Nuget by right clicking on your project, then select Manage NuGet Packages. Next, Enter NAudio at the search box => Install
C# record audio from microphone
Here's a simple c# record audio from microphone, we will record audio from our microphone then save it to a WAV file.
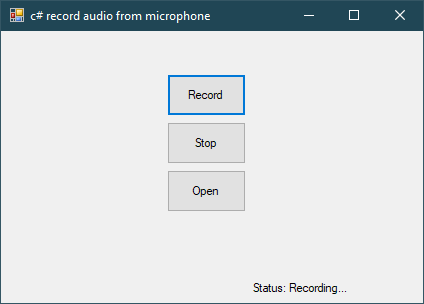
Open your form, then add your code as shown below
//c# record audio microphone WaveInEvent _waveSource; static WaveFileWriter _waveFileWriter;
Double-click on Record button, then add a click event handler to handle record audio
//c# record audio from microphone
private void btnRecord_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Set the desired audio format
_waveSource.WaveFormat = new WaveFormat(44100, 1); // 44.1kHz, mono
// Set up an event handler to capture the recorded data
_waveSource.DataAvailable += new EventHandler<WaveInEventArgs>(waveSource_DataAvailable);
// Set up the path to save the recorded audio file
string outputFilePath = $"{Application.StartupPath}\\audio.wav";
// Set up a WaveFileWriter to write the recorded data to a file
_waveFileWriter = new WaveFileWriter(outputFilePath, _waveSource.WaveFormat);
lblStatus.Text = "Status: Recording...";
// Start recording microphone c# record audio
_waveSource.StartRecording();
}Double-click on Stop button, then add a click event handler to handle stop record audio
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Stop recording
_waveSource.StopRecording();
lblStatus.Text = "Status: Recording stopped";
}Double-clicking on Open button, then add a click event handler to handle open record audio file
private void btnOpen_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
string fileName = $"{Application.StartupPath}\\audio.wav";
if (File.Exists(fileName))
{
SoundPlayer soundPlayer = new SoundPlayer(fileName);
soundPlayer.Play();
}
}Double-click on your Form , then add a Form_Load event handler to handle create a WaveInEvent
private void Form2_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Set up the WaveInEvent to record from the default sound device
_waveSource = new WaveInEvent();
}Add a FormClosing event handler to help you dispose your objects
private void Form2_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
// Clean up resources
if (_waveFileWriter != null)
_waveFileWriter.Dispose();
if (_waveSource != null)
_waveSource.Dispose();
}
// Event handler: record microphone c# audio
private static void waveSource_DataAvailable(object sender, WaveInEventArgs e)
{
// Write the recorded audio data to the WaveFileWriter
_waveFileWriter.Write(e.Buffer, 0, e.BytesRecorded);
_waveFileWriter.Flush();
}In this example:
- We create a WaveInEvent object to capture audio from the default sound device, then we set the desired audio format (44.1kHz sample rate, mono).
- Next, We set up an event handler waveSource_DataAvailable to handle the recorded audio data.
- We start recording when click on Record button.
- We stop recording when click on Stop button.
- We open recording file when click on Open button.
- Finally, we clean up the resources and close the program.
Make sure to handle exceptions appropriately and add error checking where necessary, especially when dealing with file I/O operations and audio devices.