How to use BackgroundWorker in C#
By Tan Lee Published on Jun 01, 2017 7.82K
When dealing with long-running operations that could cause delays and make your UI unresponsive, the `BackgroundWorker` class offers a convenient solution. It allows you to run tasks in the background on a separate thread, keeping the UI responsive by offloading time-consuming work from the main thread.
Open Visual Studio, then click New Project, then select Visual C# on the left, then Windows and then select Windows Forms Application. Name your project "BackgroundWorkerExample" and then click OK
How to use BackgroundWorker in a simple C# Windows Forms application.
Drag and drop the ProgressBar, Label, Button and BackgroundWorker controls from Visual Studio toolbox onto your form designer, then you can design your form as below.
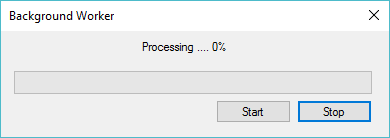
Add a click event handler to the button, then handle your code as shown below.
struct DataParameter
{
public int Process;
public int Delay;
}
private DataParameter _inputparameter;
//This event allows you to report progress to the UI. You can update your progress bar
private void backgroundWorker_ProgressChanged(object sender, ProgressChangedEventArgs e)
{
progress.Value = e.ProgressPercentage;
lblPercent.Text = string.Format("Processing...{0}%", e.ProgressPercentage);
progress.Update();
}
//This event is where the background task is executed.
private void backgroundWorker_DoWork(object sender, DoWorkEventArgs e)
{
//Set parameter
int process = ((DataParameter)e.Argument).Process;
int delay = ((DataParameter)e.Argument).Delay;
int index = 1;
try
{
for (int i = 0; i < process; i++)
{
if (!backgroundWorker.CancellationPending)
{
backgroundWorker.ReportProgress(index++ * 100 / process, string.Format("Process data {0}", i));
Thread.Sleep(delay);//used to simulate length of operation
//Add your code here...
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
backgroundWorker.CancelAsync();
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Message", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Error);
}
}
//This event is triggered when the background task completes.
private void backgroundWorker_RunWorkerCompleted(object sender, RunWorkerCompletedEventArgs e)
{
MessageBox.Show("Process has been completed.", "Message", MessageBoxButtons.OK, MessageBoxIcon.Information);
}
//Run backgroundworker
private void btnStart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (!backgroundWorker.IsBusy)
{
_inputparameter.Delay = 10;
_inputparameter.Process = 1200;
backgroundWorker.RunWorkerAsync(_inputparameter);
}
}
private void btnStop_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (backgroundWorker.IsBusy)
backgroundWorker.CancelAsync();
}DoWork: The method where the background task is performed. This runs on a separate thread, so it doesn’t block the UI.
RunWorkerCompleted: Triggered when the background task is finished. It runs on the UI thread and can be used to update the UI with the task result or handle cancellation.
ProgressChanged: This event allows for reporting progress during the background operation. You can use it to update UI elements like a progress bar.
Cancellation: The BackgroundWorker class supports cancellation through the CancelAsync() method and checking CancellationPending in the DoWork event handler.
To start the background work with the BackgroundWorker class, you use the RunWorkerAsync() method. This method triggers the execution of the task defined in the DoWork event handler on a separate background thread. Once called, the background operation begins, and you can report progress or handle completion using the relevant events (ProgressChanged and RunWorkerCompleted).
VIDEO TUTORIAL
- How to Open and Show a PDF file in C#
- How to Get all Forms and Open Form with Form Name in C#
- How to zoom an image in C#
- How to Print a Picture Box in C#
- How to update UI from another thread in C#
- How to Search DataGridView by using TextBox in C#
- How to read and write to text file in C#
- How to save files using SaveFileDialog in C#