How to Update Progress Bar from Async Task in C#
By Tan Lee Published on Jun 20, 2024 37.5K
In asynchronous programming, when you want to handle certain Task, and want to return the percentage of Task progress to display on your Progress bar.
To update a progress bar from an asynchronous task in C#, you typically need to utilize some form of event handling or callback mechanism to report the progress of the task back to the UI thread. One common approach is to use the Progress<T> class along with async and await to report progress updates.
How to use IProgress to update the Progress Bar in C#
To implement a winform progress bar with asynchronous operations in C# typically involves using Progress<T> with the IProgress<T> interface to update the UI asynchronously, you need to follow these steps.
Create a new Windows Forms Application project, then design a simple UI by dragging progress bar, button controls from your Visual Studio toolbox to your form and layout your UI as shown below.
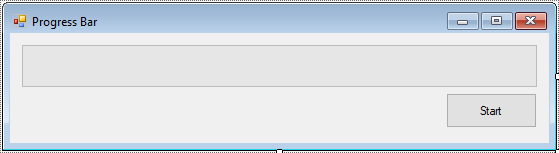
We define a method DoSomething that simulates a long-running asynchronous task, then we pass an IProgress<int> object to DoSomething. Inside DoSomething method, we report progress by calling Report on the progress reporter object.
In ReportProgress, which is the method subscribed to the progress reporter, we update the progress bar UI.
// c# winform progress bar
public void DoSomething(IProgress<int> progress)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
// Simulate some work
Thread.Sleep(100);
if (progress != null)
progress.Report(i); // progress task update c#
}
}Adding a click event handler to the Start button allows you to update a progress bar from an asynchronous task using IProgress<T>.
// c# iprogress progress bar
private async void btnStart_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// progress c# update bar
progressBar1.Value = 0;
// c# progress - create a Progress<T> instance to report progress updates
// c# task example iprogress
var progress = new Progress<int>(percent =>
{
// c# update the progress bar value
progressBar1.Value = percent;
});
// start the asynchronous operation
// c# async await progress iprogress
// progressbar async await c#
await Task.Run(() => DoSomething(progress)); // c# task
}In this example, We create a Progress<int> instance to report progress updates to the UI thread.
- Inside the
DoSomethingmethod, we loop from 1 to 100 and report progress using theprogress.Report(i)method. - Using the IProgress call back the percentage returned quickly, then update progress bar from async method. When the Start button is clicked, the progress bar value will change as the async task runs.
The IProgress<T> interface is commonly used to report progress from an asynchronous operation, such as a background task, to the UI thread or to other parts of your application.
For example, How to use IProgress<T> with a Task.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// c# task example iprogress
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
// Create an instance of IProgress<int>
IProgress<int> progress = new Progress<int>(percent =>
{
// This callback will be invoked with progress updates
Console.WriteLine($"Progress: {percent}%");
});
// Call the method to start a long-running task with progress reporting
await DoWorkAsync(progress);
Console.WriteLine("Work completed!");
}
static async Task DoWorkAsync(IProgress<int> progress)
{
// Simulate a long-running task
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
// Simulate some work
await Task.Delay(100);
// Report progress
progress.Report(i);
}
}
}Output in Console
Progress: 0% Progress: 1% Progress: 2% ... Progress: 100% Work completed!
Remember, Report method can be called from any thread, as Progress<T> internally handles synchronization for you, ensuring safe access to the progress data.