How to sign a powershell script
By Tan Lee Published on Oct 02, 2024 1.02K
PowerShell scripts are useful for automating tasks on Windows, but running unsigned scripts can result in errors like "PowerShell not digitally signed." To prevent these issues, it's important to sign your scripts with a digital certificate.
How to sign a powershell script?
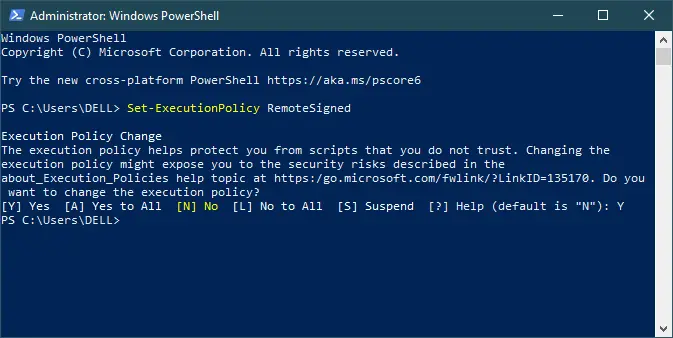
First, Open your Windows PowerShell
Ensure that your execution policy allows for signed scripts.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
| Execution Policy | Description | Scope of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Restricted | No scripts allowed to run | Default on Windows |
| AllSigned | Only runs scripts signed by a trusted publisher | Recommended for most users |
| RemoteSigned | Requires remote scripts (Internet) to be signed | Flexible yet secure option |
| Unrestricted | No restrictions on script execution | Not recommended due to security risks |
| Bypass | Ignores all execution policies | Should be used with extreme caution |
You need a code signing certificate. This can be obtained from a Certificate Authority (CA) or you can create a self-signed certificate for testing purposes.
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName "FoxLearn" -CertStoreLocation "cert:\CurrentUser\My"
Output:
Thumbprint Subject
---------- -------
CBD7ACE757B43A09465D4454FCF590D82079D380 CN=FoxLearn
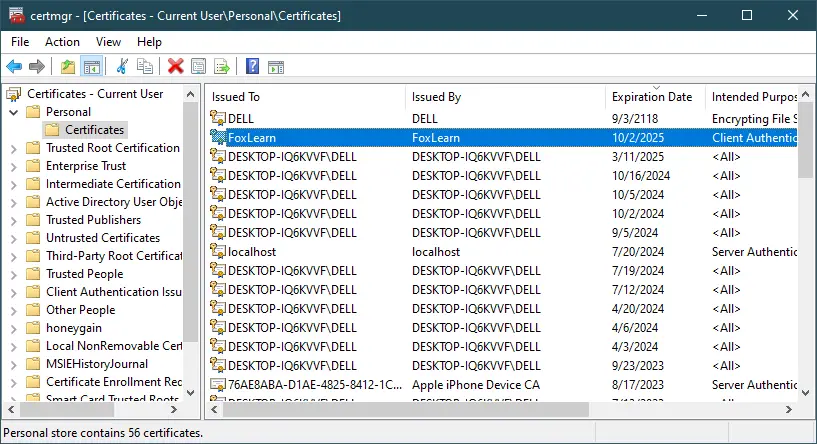
After running the command, you can find your certificate in the certmgr.msc under "Personal" -> "Certificates".
Retrieve the certificate you just created or obtained.
$cert = Get-ChildItem Cert:\CurrentUser\My | Where-Object { $_.Subject -match "FoxLearn" }Use the Set-AuthenticodeSignature cmdlet to sign the script.
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath "C:\YourPath\script.ps1" -Certificate $cert
You can check if the script is signed correctly with
Get-AuthenticodeSignature "C:\YourPath\script.ps1"
If you use a self-signed certificate, remember that it will not be trusted by default on other systems. You may need to install the certificate into the trusted root certification authorities store on those systems.
You can open PowerShell as an admin and run the command.
#Certificate name
$name = "FoxLearn"
# Create a self-signed certificate
$cert = New-SelfSignedCertificate -CertStoreLocation Cert:\CurrentUser\My -Subject "CN=$name" -KeySpec Signature -Type CodeSigningCert
#Export the Certificate to "Documents" Folder in your computer
$path = [Environment]::GetFolderPath("MyDocuments")+"\FoxLearn.cer"
Export-Certificate -Cert $cert -FilePath $path
#Add Certificate to the "Trusted Root Store"
Get-Item $path | Import-Certificate -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\Root"
Write-host "Certificate Thumbprint:" $Certificate.ThumbprintSigned powershell scripts
$thumbprint = "CBD7ACE757B43A09465D4454FCF590D82079D380"
$path = "C:\YourPath\script.ps1"
#Get the Certificate from Cert Store
$CodeSignCert = Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\CurrentUser\My | Where-Object {$_.Thumbprint -eq $thumbprint}
#Sign the PS1 file
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath $path -Certificate $CodeSignCert
To extend the lifespan of your PowerShell script's signature, you can include an optional timestamp when signing it. This ensures that the script remains valid even after the signing certificate expires.
$cert = Get-ChildItem -Path Cert:\CurrentUser\My | Where-Object {$_.Thumbprint -eq $thumbprint}
Set-AuthenticodeSignature -FilePath "C:\YourPath\script.ps1" -Certificate $cert -TimestampServer "http://timestamp.digicert.com"If you open the signed PS1 file, you’ll find the encrypted signature.
- How to Get a file’s MD5 checksum
- How to delete a Windows service in PowerShell
- How to run powershell commands in C#
- How to execute PowerShell script in C#
- How to display GUI Message Boxes in PowerShell
- How to run powershell script using task scheduler
- How to run powershell script from cmd
- How to download file from url in PowerShell